Parkinson’s disease – Foods to have and avoid
Parkinson’s disease affects a large number of individuals in the country. It is characterized by tremors and rigid muscles and affects the day-to-day functioning of the individual. No specific nutritional program can help cure Parkinson’s disease. But research has shown that following a healthy meal plan and nurturing a healthy body can help deal with the condition better. Herein, we shall discuss the foods that help tackle Parkinson’s as well as those to be avoided.
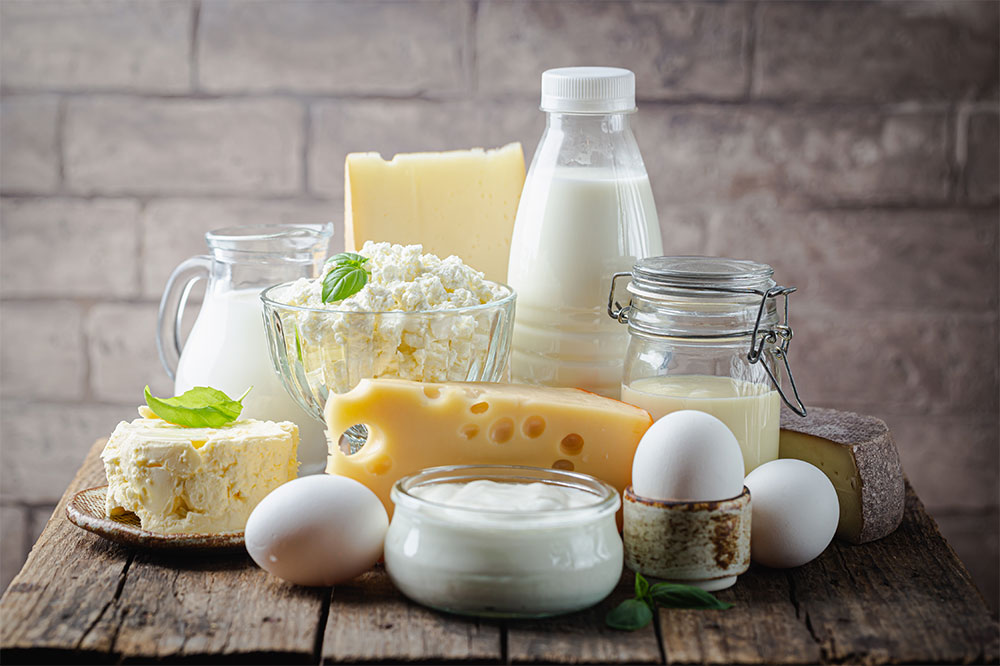

These foods are highly recommended for Parkinson’s disease patients:
Fatty fish
Fatty fish can go a long way in helping tackle Parkinson’s disease. The omega-3 fatty acids present in fatty fish can help reduce inflammation of the nerves and improve neurotransmission. Omega-3s can also help slow the progression of neurodegeneration due to Parkinson’s disease.
Foods high in antioxidants
Free radicals can damage organs and fatty tissue, and even lead to the development of Parkinson’s in the body. Antioxidants help tackle free radicals that wreak havoc in the body. Blueberries, grapes, strawberries, and citrus fruits are great sources of antioxidants.
Foods with high nutritional value
Those who suffer from Parkinson’s disease also suffer from nutrient deficiencies. To tackle this issue, eating foods with tons of zinc, iron, and essential vitamins becomes cricial. Maintaining a healthy nutritional regimen goes a long way when it comes to fighting this degenerative disease.
Certain foods can do more damage and can actually increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Here are a few of them:
Processed foods
Having a lot of processed foods can increase the severity of symptoms in Parkinson’s disease patients. Common processed foods include canned foods, breakfast cereals, bacon, and candies.
Foods with high saturated fats
Certain studies have suggested that having foods with saturated fats or cholesterol can increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. Although the link between such foods and this condition remains to be confirmed, avoiding foods with high saturated fats is best for leading an overall healthy lifestyle.
Aside from food, certain medication can help tackle Parkinson’s disease, such as
Levodopa
This medication is prescribed to almost every individual who suffers from Parkinson’s disease. Common side effects of taking include Levodopa dizziness and exhaustion.
ONGENTYS®
Ongentys is an add-on oral medication that is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Common side effects of taking this medication include constipation, weight loss, and dryness.
RYTARY®
RYTARY, a treatment option for Parkinson’s disease, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2015. It is a prescription medication available in capsule form and contains levodopa with carbidopa. Levodopa converts to dopamine, the missing chemical in Parkinson’s whereas carbidopa decreases levodopa’s side effects. RYTARY is a well-tolerated Parkinson’s treatment option useful for reducing motor symptoms like tremors, spasms, and stiffness. Common side effects include nausea, low blood pressure, hallucinations, and dyskinesia.
FYCOMPA
Clinical evidence suggests that FYCOMPA (perampanel) for Parkinson’s is beneficial in treating epileptic attacks or keeping the symptoms under check. The medication is supposed to be taken orally every day and the dose is adjusted according to the symptoms presented by the patient. FYCOMPA for Parkinson’s Rx can be filled in via online pharmacies using coupon codes available on their websites. Additionally, the FYCOMPA website has a special card program that helps save on the medicine and provides easier access to it.